Comportamiento clínico epidemiológico de la cefalea migrañosa en la infancia
Resumen
Introducción: la migraña es la causa más frecuente de cefalea en la infancia.
Objetivo: caracterizar el comportamiento clínico epidemiológico de la cefalea migrañosa en la infancia.
Material y Método: se realizó un estudio epidemiológico, longitudinal y prospectivo durante el año 2009. Del universo de pacientes que asistieron a la consulta de neuropediatría del Hospital General Docente "Comandante Pinares" de San Cristóbal, provincia de Pinar del Río por presentar cefalea, la muestra la conformaron 115 niños con edades comprendidas entre 4 y 15 años que cumplían con criterios diagnósticos de migraña, el tipo de muestreo fue intencional. La información necesaria se obtuvo a través de una encuesta que contempla variables como datos generales de identidad, localización y carácter del dolor. Para la valoración estadística se utilizó la media porcentual y la prueba de hipótesis de ji cuadrado por un sistema computarizado.
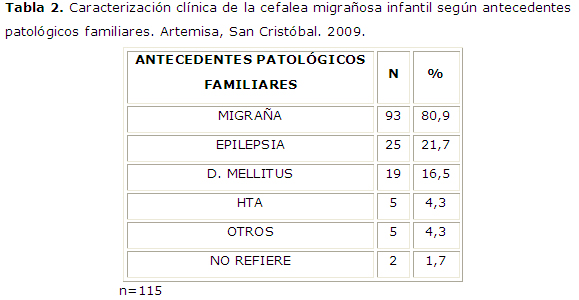
Resultados: se pudo comprobar que la incidencia de migraña en el sexo femenino aumenta con la edad, los antecedentes familiares estuvieron presentes en el 80,9% de los pacientes.
Conclusiones: el dolor en la hemicránea, de carácter pulsátil fue más frecuente en niños mayores de 10 años mientras que en los menores de 10 años predominó la localización frontal así como el carácter no pulsátil del dolor.
Palabras clave
Referencias
Rodríguez Tudela A, Cárdenas Giraudy A. Comportamiento de la cefalea migrañosa: interconsulta de proyección comunitaria. Rev Cubana Pediatr.[Internet]. 2008 [citado junio 2011]; 80(2). Disponible en: http://bvs.sld.cu/revistas/ped/vol80_2_08/ped08208.htm
Cárdenas Giraudy AG, Pozo Lauzán D, García Martínez D, González Vázquez E, Agramonte Pereira C. Migraña: estudio de los factores de riesgo de las crisis en niños y adolescentes. Rev Cubana Pediatr. [Internet]. 2008 [citado junio 2011]; 80(3). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0034-75312008000300001&script=sci_arttext
Vannatta Kathryn A, Getzoff EA, Powers Scott W, Noll Robert B, Gerhardt CA, Hershey AD, et al. Multiple Perspectives on the Psychological Functioning of Children With and Without Migraine. Headache. [on line] 2008 [cited june 2011]; 48(7): [About. 10p.]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.01051.x/full
Villa TR, Correa Moutran AR, Sobirai Diaz LA, Pereira Pinto MM, Carvalho FA, Gabbai AA, et al. Visual attention in children with migraine: a controlled comparative study. Cephalalgia. [on line] 2009 [cited june 2011]; 29(6): [About. 3p.]. Available from: http://cep.sagepub.com/content/29/6/631.long
Cuvellier Jean-Christophe , Carvalho Sandra, Mars Amaury, Auvin S. Study on management of pediatric migraine by general practitioners in northern France. J Headache Pain. [on line]. 2009 [cited june 2011]; 10(3): [About. 8p.]. Available from: http://www.springerlink.com/content/h4754n2t374391x6/fulltext.pdf
Eidlitz-Markus T, Gorali O, Haimi-Cohen Y, Zeharia A. Symptoms of migraine in the paediatric population by age group. Cephalalgia. [on line]. 2008 [cited june 2011]; 28(12): [About. 4p.]. Available from: http://cep.sagepub.com/content/28/12/1259.long
Arroyo Hugo A. Migraña y otras cefaleas primarias en la infancia y la adolescencia: La nueva clasificación internacional de cefaleas (II edición) de la sociedad internacional de cefaleas. Medicina (B. Aires). [Internet]. 2007 [citado 2011 Sep 08]; 67(6): [Aprox. 7p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.ar/scielo.php?pid=S0025-76802007000700011&script=sci_abstract
Donald WL. Headaches in Children and Adolescents. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. [on line]. Cuba; 2007 [cited june 2011]. Available from: http://www.sld.cu/galerias/pdf/sitios/pediatria/headaches_in_children_and_adolescents.pdf
Cuvellier JC, Donnet A, Guégan-Massardier É, Nachit-Ouinekh F, Parain D, Vallée L. Clinical features of primary headache in children: a multicentre hospital-based study in France. Cephalalgia. [on line]. 2008[cited june 2011]; 28(11): [About. 8p.]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01656.x/abstract
Chakravarty A, Mukherjee A, Roy D. Migraine pain location: how do children differ from adults? J Headache Pain. [on line]. 2008 [cited june 2011]; 9(6): [About. 2p.]. Available from: http://www.springerlink.com/content/700mu877368231x7/fulltext.pdf
Prensky A, Sommer D. Diagnosis and treatment of migraine in children. Neurology. [on line]. 1979 [cited june 2011]; 29(4): [About. 4p.]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/571549
Gabmann J, Morris L, Heinrich M , Kröner-Herwig B. One-year course of pediatric headache in children and adolescents aged 8_15 years. Cephalalgia. [on line]. 2008 [cited june 2011]; 28(11): [About. 8p.]. Available from: http://cep.sagepub.com/content/28/11/1154.long
Akyol A, Kiylioglu N, Aydin I, Erturk A , Kaya E , Telli E, et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of migraine among school children in the Menderes region. Cephalalgia. [on line]. 2007 [cited june 2011]; 27(7): [About. 6p.]. Available from: http://cep.sagepub.com/content/27/7/781.long
Kröner-Herwig B, Heinrich M, Morris L. Headache in German children and adolescents: a population-based epidemiological study. Cephalalgia. [on line]. 2007 [cited june 2011]; 27(6): [About. 8p.]. Available from: http://cep.sagepub.com/content/27/6/519.long
Bruijn J, Locher H, Passchier J, Dijkstra N , Willem F. Psychopathology in Children and Adolescents With Migraine in Clinical Studies: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics. [on line]. 2010 [cited june 2011]; 126(2): [About. 9p.]. Available from: http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/126/2/323.full.pdf+html
Del Zotto E, Pezzini A , Giossi A , Volonghi I, Padovani A. Migraine and ischemic stroke: a debated question. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. [on line]. 2008 [cited june 2011]; 28(8): [About. 22p.]. Available from: http://www.nature.com/jcbfm/journal/v28/n8/full/jcbfm200836a.html
Diener HC, Küper M, Kurth T. Migraine-associated risks and comorbidity. J Neurol. [on line]. 2008 [cited june 2011]; 255(9): [About. 11p.]. Available from: http://www.springerlink.com/content/k14w37486x083230/fulltext.pdf
Haan J, Hollander J, Ferrari MD. Migraine in the elderly: a review. Cephalalgia. [on line]. 2007 [cited june 2011]; 27(2): [About 9p.]. Available from: http://cep.sagepub.com/content/27/2/97.long
Kneževi?-Pogan?ev M. Epidemiology, Characteristics and Distinctiveness of Headaches in Children from Vojvodina, Serbia. Neuroepidemiology. [on line]. 2008 [cited june 2011]; 31(2): [About. 6p.]. Available from: http://content.karger.com/produktedb/produkte.asp?DOI=000151513&typ=pdf
Rossi N L, Vajani S, Cortinovis I, Spreafico F, Menegazzo L. Analysis of the International Classification of Headache Disorders for diagnosis of migraine and tension type headache in children. Neurology. [on line]. 2008 [cited june 2011]; 50(4): [About. 5p.]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.02041.x/pdf
Bruijn J. Quality of life and psychological functioning in observational and intervention studies. [Internet]. Erasmus Medical University Centre, Nederland; september 2010 [cited june 2011]. Available from: http://repub.eur.nl/res/pub/20821/100929_Bruijn,%20Jacques%20Klaas%20Jan.pdf
Copyright (c) 2012 Liudmila de la Cariadad Riesgo Mayea, Yaimara Dorta Correa, Juan Carlos Cruz Robaina, Alexis Pérez Soler, Efrén Padrón Iglesias

Esta obra está bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional.







 La revista está: Certificada por el CITMA
La revista está: Certificada por el CITMA