Endarterectomía de carótidas con analgesia acupuntural
Palabras clave:
Endarterectomia de carótidas, Analgesia por acupuntura, Ataque isquémico transitorio.Resumen
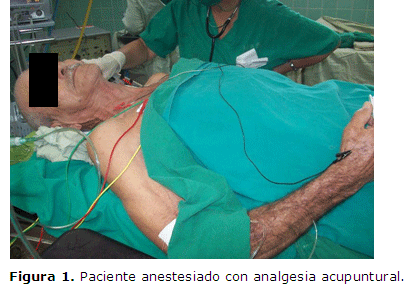
La enfermedad carotídea aumenta significativamente el riesgo de tener el tipo más común de ataque isquémico cerebral (Ictus). Es sobradamente conocido los elevados procesos isquémicos cerebrales que tienen su origen en lesiones estenosantes (ulceradas o no) de las arterias extracraneales, fundamentalmente en la bifurcación carotídea. Dado que estas lesiones tienen acceso quirúrgico el tratamiento de rutina desde hace años es la Endarterectomia Carotídea. El efecto analgésico de la acupuntura permite realizar cualquier tipo de operación en la región anatómica seleccionada, conservando el paciente su lucidez mental, algo oportuno para determinar que pacientes necesitarán de shunt intraluminal después del clampeo de las arterias durante esta operación.Con el objetivo de asociar estos criterios, a un paciente masculino de 76 años que había sufrido cuatro ataques cerebrales de isquemia, producto de placa de ateroma complicada y estenosante de la bifurcación carotidea izquierda, se le realizó una endarterectomía con analgesia acupuntural sin complicaciones transoperatorias ni posoperatorias, por lo que se propone que es una alternativa lógica, económica y segura de realizar la desobstrucción carotídea.
Descargas
Citas
1. Silva Sieger F, Arenas Borda W, Zarruk Serrano JG. Factores asociados con enfermedad cerebro vascular isquémica. Rev. de NeurologÃa. Marzo, 2007; 44(5): 259-264.
2. Dobson Ej, Featherstone Rl, Bonati Lh, Vander Worp HB, et al. Carotid artery stenting compared with endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis (International Carotid Stenting Study): an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. [Internet] 2010; 375: 985-997. [citado 5 de abril de 2013]. Disponible en: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2755037/
3. Bond R, Rerkasem K, Naylor R, Rothwell PM. Diferentes tipos de parches para la angioplastia carotÃdea con parches. [Internet] 2010. [citado 5 de abril de 2013]. La Biblioteca Cochrane Plus[internet]. 2013[citado marzo 2013]; 5: Disponible en: http://www.update-software.com/BCP/BCPGetDocument.asp?DocumentID=CD000071
4. Jiménez E, Oteros R, Delgado F, Cano A. Manejo actual de la estenosis de carótida: Tratamiento endovascular comparado con endarterectomÃa. Revista Chilena de RadiologÃa. [Internet]. 2012[citado 5 de abril de 2013];18(2): 49-57. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.cl/pdf/rchradiol/v18n2/art03.pdf
5. Ballesteros Pomar M, Peña Cortés R, Alonso Argüeso G, Ortega MartÃn J.M, Fernández Morán C, Vaquero Morillo F. SÃndrome hiperperfusión cerebral: ¿complicación infrecuente de la endarterectomÃa carotÃdea?. AngiologÃa [Internet]. 2011[citado 5 de abril de 2013]; 63(5):193-199. Disponible en: http://www.elsevier.es/es/revistas/angiologia-294/sindrome-hiperperfusion-cerebral-complicacion-infrecuente-endarterectomia-carotidea-90034949-originales-2011
6. Villarreal Careaga J, Murillo Bonilla L, Góngora Rivera F, Leyva Rendón A, Barinagarrementeria F, et al. GuÃa clÃnica para el tratamiento quirúrgico (endarterectomÃa) y endovascular (angioplastia con protección distal y colocación de stent) para la prevención secundaria de la isquemia cerebral asociada a enfermedad ateroesclerosa carotÃdea. Revista de Investigación ClÃnica [Internet]Marzo-Abril 2010; 62(2): 170-180[citado 5 de abril de 2013]. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/revinvcli/nn-2010/nn102k.pdf
7. Pagola Bérger V. Historia de la analgesia quirúrgica acupuntural. En: Analgesia Quirúrgica Acupuntural. México: Editorial Herbal, 2005. p. 4-20
8. Pagola Bérger V, Llovera RodrÃguez JL, Pérez Borges N. La Analgesia Quirúrgica Acupuntural en cirugÃa del cuello y cara. Medicentro [Internet]. 2006 [citado 5 de abril de 2013]; 10(4): [aprox.5p]. Disponible en: http://www.sld.cu/galerias/pdf/sitios/mednat/la_analgesia_quirurgica_acupuntural_en_la_cirugia_del_cuello_y_la_cara.pdf
9. Marquardt L, Geraghty OC, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM. Low Risk of Ipsilateral Stroke in Patients With Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis on Best Medical Treatment. A Prospective, Population-Based Study. Stroke. [Internet] 2010; 41(1): e11-17. [citado 5 de abril de 2013]. Disponible en: http://stroke.ahajournals.org/content/41/1/e11.full
10. Field TS, Benavente OR. Current status of antiplatelet agents to prevent stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011; 11(1): 6-14.
11. Palacios RJM y cols. Angioplastia carotÃdea con stent en un centro hospitalario de México. Resultados y seguimiento a largo plazo. Revista Mexicana de CardiologÃa.Enero - Marzo 2011; 22(1):10-16
12. Brott TG, Hobson RW , Howard G, Roubin GS, Clark WM et al. The CREST Investigators. Stenting versus Endarterectomy for Treatment of Carotid-Artery Stenosis. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2010 [citado 5 de abril de 2013]; 363: 11-23. Disponible en: http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa0912321
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación esta revista.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).


