Diseño de un software para la enseñanza de la asignatura Programación y Gestores de Bases de Datos en la carrera de Tecnología de la Salud
Palabras clave:
Programas informáticos/normas/clasificación.Resumen
Introducción: la computadora y el software educativo, como medios de enseñanza resulta un eficiente auxiliar del profesor en la preparación y desarrollo de las clases.
Objetivo: diseñar un software sobre programación y Gestores de Bases de datos, para mejorar el proceso de preparación de estudiantes, profesores y tutores dela carrera Sistemas de Información en Salud.
Material y método: se realizó una investigación aplicada (desarrollo tecnológico) y prospectiva, en la Filial de Tecnología: "Simón Bolívar" de Pinar del Río, utilizando como principales métodos: histórico-lógico, la revisión de documentos y la modelación, basándonos en la metodología de ingeniería de software que se aplica actualmente y contando con el criterio del profesor principal de la asignatura.
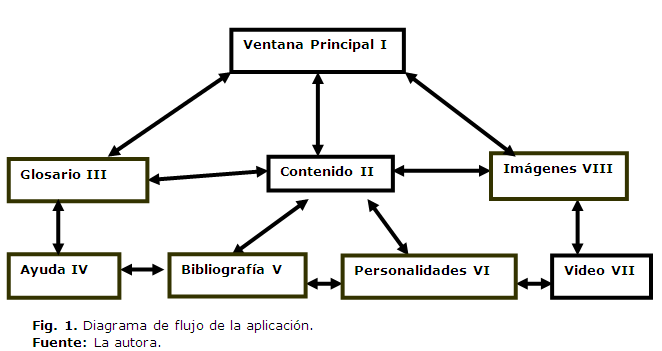
Resultados: se obtiene el criterio de los estudiantes en cuanto a diseño, nuevas formas de motivación y selección de recursos de multimedia para insertar en este producto, así como el desarrollo de algunos elementos de ingeniería de software que se aplican en las cartas tecnológicas para este tipo de diseño, en la obtención de cada uno de los objetos a crear y sus propiedades facilitando su ubicación en la interfaz descrita.
Conclusiones: este diseño de software es de gran importancia para la creación del software que se describe y que será utilizado en las clases de la carrera, ya que proporciona un medio de motivación y aprendizaje, mejor gestión de la información y facilita la preparación de profesores y estudiantes en cualquier momento.
Descargas
Citas
1. Edel-Navarro R. Entornos virtuales de aprendizaje: la contribución de "lo virtual" en la educación. Revista mexicana de investigación educativa. [Internet] 2010 [Citado 20 de abril de 2012]; 15(44): [Aprox. 8p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S1405-66662010000100002lng=estlng=es
2. Jerez Naranjo YV, GarofaloHernandez AA. Aprendizaje basado en tareas aplicado a la enseñanza de las Telecomunicaciones.EAC [Internet] 2012 [Citado 20 de abril de 2012]; 33(3). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S1815-59282012000300001lng=esnrm=iso
3. Tendencias de la aplicación de las nuevas tecnologías de la Información y la Comunicación en el mejoramiento del proceso de enseñanza. Association of Research Libraries. Definition and Purposes of a Digital Library. [Internet]. 2002 [citado 12 Mayo 2010]; 30(1): [aprox. 3 p]. Disponible en: http://sunsite.berkeley.edu/ARL/definition.html
4. Careaga Butter MY. Fundamentos acerca de un modelo cibernético de Educación. La Habana: Pueblo y Educación; 2002. p.5.
5. Cervantes Montero G, Milán Palmer M. La informática educativa como medio de enseñanza. Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo. [Internet] 2011 [Citado 20 de abril de 2012]; 3(28). Disponible en: http://www.eumed.net/rev/ced/28/cmmp.htm
6. Labañino Rizzo C. Guía de evaluación de hiperentornos de aprendizaje. La Habana: Ministerio de Educación; 2009.
7. Cabello R, Morales S, Feeney S. La incorporación de medios informáticos en la enseñanza: políticas y propuestas para la formación docente. Argentina: Universidad Nacional de General Sarmiento y Universidad Nacional de Córdoba; 2009. Disponible en: http://www.razonypalabra.org.mx/anteriores/n52/32CabelloMoralesyFeeney.pdf
8. López Y. Diseño de un Programa Computacional Educativo (Software) para la Enseñanza de Balance General. Formación universitaria. [Internet] 2011 [Citado 20 de abril de 2012]; 4(3): [Aprox. 7p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S0718-50062011000300004lng=estlng=es
9. Serrano JE, Narváez PS. Uso de Software Libre para el Desarrollo de Contenidos Educativos. Formación universitaria. [Internet] 2010 [Citado 20 de abril de 2012]; 3(6): [Aprox. 9p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S0718-50062010000600006lng=estlng=es
10. Vidal Ledo M, Gómez Martínez F, Ruiz Piedra AM. Software educativos. Educ Med Super[Internet]. 2010 Mar[citado 2013 Nov 05]; 24(1): [Aprox. 13p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S0864-21412010000100012lng=es
11. Flores Muro B, Contreras Delgado CE. Modelo de investigación, aplicado en el desarrollo de software. Caso de estudio en instituciones publicas de educación superior, Saltillo, Coahuila México. Revista de Estudos Politécnicos. [Internet]. 2008 [citado 2013 Nov 05]; 6(9): [Aprox. 24 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.oces.mctes.pt/pdf/tek/n9/n9a12.pdf
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación esta revista.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).


