Intervention strategy about diabetologic a education and chronic renal failure in type 2 diabetics
Keywords:
Diabetes mellitus, Chronic renal insufficiency, Oxidative stress, Health education.Abstract
Introduction: diabetes mellitus and the chronic renal failure are in their evolution associated to the oxidative stress, a reason why diabetologic education on the knowledge regarding this relation must result in a better control of diabetes and lower risk of diabetic nephropathy. Objective: to evaluate the effectiveness of an educational intervention on type 2 diabetic patients about oxidative stress and chronic renal failure in the medical office number 10 of Hermanos Cruz University Outpatient Polyclinic of Pinar del Río.
Material and method: an applied, quantitative, longitudinal, prospective, quasi-experimental research of intervention was carried out in the medical office number 10 of Hermanos Cruz University Outpatient Polyclinic, in the period from April 1 to September 15 2013. The sample group of 56 type 2 diabetic patients was studied. Descriptive statistics techniques were used as well as the McNemar chi-square test.
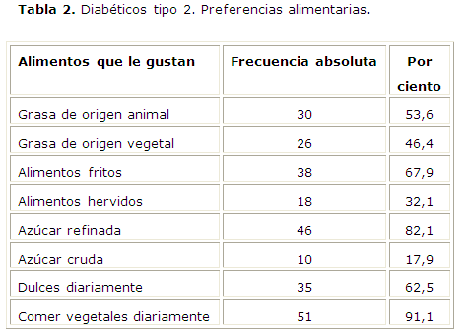
Results: the predominating group was that of 60-69 years old. After applying the strategy, the sheer number of patients knew about the existence of the relationship among diabetes mellitus, chronic renal failure and smoking. The highest majority knows about the concept of oxidative stress associated to the disease, and also the existence of kidney affections in the diabetic patients and the importance of salt, sugar, oil, and vegetables adequate consumption. Among the food habit there was a predominance of vegetable sans white sugar. Conclusions: high blood pressure and obesity constitute, of the diseases with intense oxidative stress, the most frequent of the studied group. After applying the strategy, the total number of the patients improved the level of knowledge about their disease.
Downloads
References
1. Rosales González E, Crespo Mojena N, Triana Ponce A, Triana López Y, Palma López M E. Causas de muerte en pacientes diabéticos de Ciudad de La Habana según certificados de defunción. Revista Cubana de Medicina General Integral [periódico de la Internet]. Enero-Marzo 2008[citado 2009 Mar 15]; 24(1). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S0864-21252008000100003lng=esnrm=isotlng=es
2. Alfonso Guerra JP, Pérez Caballero MD, Hernández Cueto MJ, García Barreto D. Hipertensión arterial en la atención primaria de salud. 1ra edición. La Habana: ECIMED; 2009.
3. Alfonso Guerra JP. Usted puede... Controlar su hipertensión. 1ra edición. La Habana: Editorial Científico-Técnica; 2010.
4. Castañer Moreno J, Hurtado de Mendoza Amat J, Fuentes Abreu J, Montero González T, Teuma Cortes I, Capote Pereira L, et al. Diagnóstico de daño renal crónico terminal en autopsias. Rev Cub Med Mil [Internet] 2010 Marzo-Junio [citado 2013 marzo 5]; 39(2). Disponible en: http://www.bvs.sld.cu/revistas/mil/vol39_2_10/mil02210.htm
5. Morales Rigau JM, González Pino M, García Betancourt N, Acebo Figueroa F. Prevalencia de insuficiencia renal crónica mediante las fórmulas de Cockcroft-Gault y Modificación de Dieta en la Enfermedad Renal. Matanzas. 2010. Rev. Med. Electrón. [Internet] 2012 Julio Agosto [citado 2013 marzo 5]; 34(4). Disponible en: http://www.revmatanzas.sld.cu/revista%20medica/ano%202012/vol4%202012/tema05.htm
6. Vicente Peña E, Rodríguez Porto AL, Sánchez Zulueta E, Quintana López L, Riverón González JM, Ledo Grogués D, et al. Diagnóstico y tratamiento en medicina interna. 2da edición. La Habana: ECIMED; 2012.
7. Moehlecke M, Leitão CB, Kramer CK, Rodrigues TC, Nickel C, Silveiro SP et al. Effect of metabolic syndrome and of its individual components on renal function of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Braz J Med Biol Res, July 2010[citado 2013 abril 5]; 43(7): 687-693. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S0100-879X2010000700012
8. Arce Bustabad S, Almaguer López M, Herrera Valdés R, Magrans Bush Ch, Benítez Llanes O, Reyes Arencibia R, et al. Trasplante renal y enfermedad renal crónica. 1ra edición. La Habana: ECIMED; 2009.
9. Cruz MC, Andrade C, Urrutia M, Draibe S, Nogueira-Martins LA, Cintra Sesso RC. Quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clinics [Internet] 2011[citado 2013 marzo 5]; 66(6). Disponible en: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_pd&pid=S1807-59322011000600012lng=esnrm=isotlng=en
10. Gómez R, Monteiro H, Cossio-Bolaños MA, Fama-Cortez D, Zanesco A. El ejercicio físico y su prescripción en pacientes con enfermedades crónicas degenerativas. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Pública. [Internet] 2010 [citado 2013 marzo 5]; 27(3): 379-86. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S1726-46342010000300011lng=esnrm=isotlng=es
11. Andrade-Rodríguez HJ, Valadez-Castillo FJ, Hernández-Sierra JF, Gordillo-Moscoso AA, Dávila-Esquedac ME, Díaz-Infante CL. Efectividad del ejercicio aeróbico supervisado en el nivel de hemoglobina glucosilada en pacientes diabéticos de tipo 2 sedentarios. Gaceta Médica Mexicana. [Internet] 2007[citado 2013 marzo 5]; 143(1): 11-5. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/gaceta/gm-2007/gm071c.pdf
12. Martins Vancea DM, Vancea JN, Fernandes Pires MI, Reis MA, Brandão Moura R, Atala Dib S. El efecto de la frecuencia del ejercicio físico en el control glucémico y composición corporal de diabéticos tipo 2. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia [internet] 2009 Enero [citado 2011 mayo 21]; 92(1). Disponible en: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttextpid=S0066-782X2009000100005lng=esnrm=isotlng=es
13. Deakin T, McShane CE, Cade JE, Williams RDRR. Entrenamiento grupal de estrategias de autocuidado en personas con diabetes mellitus tipo 2(Revisión Cochrane) Biblioteca Cochrane Plus, Número 2, 2008 [base de datos en internet]. Oxford: Update Software Ltd; [Internet] 2008-[citado 2011 mayo 26]. [aproximadamente 69 pantallas]. Disponible en: http://cochrane.bvsalud.org/cochrane/show.php?db=reviewsmfn=1803id=CD003417lang=esdblang=lib=BCP
14. Vermeire E, Wens J, Van Royen P, Biot Y, Hearnshaw H, Lindenmeyer A. Vermeire E, Wens J, Van Royen P, Biot Y, Hearnshaw H, Lindenmeyer A. Intervenciones para mejorar el cumplimiento de las recomendaciones de tratamiento en personas con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (Revisión Cochrane traducida). La Biblioteca Cochrane Plus. 2008; 4. Disponible en: http://cochrane.bvsalud.org/cochrane/show.php?db=reviewsmfn=1973id=CD003638lang=esdblang=lib=BCP
15. Durán A, Martín P, Runkle I, Pérez N, Abad R, Fernández M et al. Benefits of self-monitoring blood glucose in the management of new-onset Type 2 diabetes mellitus: The St Carlos Study, a prospective randomized clinic-based interventional study with parallel groups. Journal of Diabetes [periódico de la internet] 2010[citado 2011 mayo 26]; 2(3): 203-11. Disponible en: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1753-0407.2010.00081.x/full
16. Planas Vilà M. Puesta al día sobre el paciente diabético/síndrome metabólico. [monografía en Internet] Badajoz: Aula médica ediciones (Grupo Aula Médica, S.L.) [Internet]. 2010[citado 2010 Jul 10]. Disponible en: http://www.nutricionhospitalaria.com/pdf/4796.pdf
17. Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, et all. Harrison Principios de Medicina Interna, 17a edición. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.; 2009.
18. Alarcon Chambi MI, Aguilar Huarita RW, Alejo Soliz CM, et al. Factores de riesgo asociados a Nefropatía Diabética en pacientes ingresados a hemodiálisis del Hospital Viedma desde enero de 2006 hasta enero de 2012. Rev Cient Cienc Méd, [Internet] 2012[citado 2010 Jul 10]; 15(2): 12-17. Disponible en: http://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=4179547
19. Sánchez Mojarrieta M, Jerez Fernández E. Estrés oxidativo y radicales libres ¿Amigos o enemigos? 1ra edición. Pinar del Río: Ediciones Loynaz; 2012.
20. Forbes JM, Coughlan MT, Cooper ME. Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. America Diabetes Association 2008; 57(6): 1446-54. Disponible en: http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/57/6/1446.full
21. Instituto de Nutrición e Higiene de los Alimentos, Viceministerio de Higiene y Epidemiologia, Ministerio de Salud Pública de Cuba (colectivo de autores). Alimentación, nutrición y salud. Habana: Cámara del Libro; 2011.
22. Cignarelli M, Lamacchia O, Di Paolo S, Gesualdo L. Cigarrette smoking and kidney dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J Nephrol. 2008 Mar-Apr;21(2):180-9.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


