Sublingual ranula in a newborn
Keywords:
Mucocele, Ranula, Newborn infant.Abstract
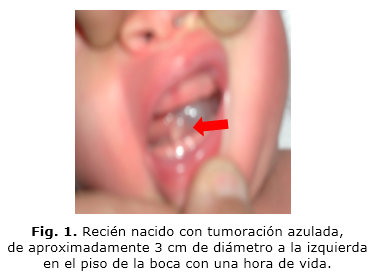
Introduction: mucocele and ranula are cysts of mucous retention, localized in the oral cavity where minor salivary glands are located.Case report: a term newborn, good weight, male sex, second twin by cesarean section. At birth on physical examination a blue tumor is observed in the floor of the mouth which made baby’s feeding difficult, without causing respiratory disorders. According to the clinical evolution, at 5 days old, the mother observed a spontaneous diminution of volume in the base of tongue, though feeding problems persisted. A congenital sublingual ranula was diagnosed. After a multidisciplinary assessment the baby was discharged with follow-up due to this high-risk condition. Currently the baby is healthy, and presents a good psychomotor development and no relapses.
Conclusions: the newborn improved spontaneously without health compromise or needing surgical procedures.
Downloads
References
1. Santana Garay JC. Atlas de patología del complejo bucal. 2 ed. La Habana, Cuba: Editorial Ciencias Médica; 2010. p. 495-548.
2. Rios Livia TM, Araujo JE, Nardozza LM, Moron AF, Martins MG. Rânula congênita: diagnóstico ultrassonográfico antenatal. Radiol Bras[Internet]. 2012[citado 14 september 2013]; 45(5): [aprox. 1p.]. Disponible en: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-39842012000500015
3. Angulo-Espinoza MA, Ángeles ET, Gutiérrez AD. El diagnóstico del pediatra ante la patología bucal benigna del recién nacido. Acta Pediatr Mex[Internet]. 2013[citado 14 september 2013]; 34: [aprox. 8p.]. Disponible en: http://new.medigraphic.com/cgi-bin/resumen.cgi?IDREVISTA=74&IDARTICULO=44777&IDPUBLICACION=4628
4. Arvind S, Pooja S, Amit S. Congenital Ranula in a Newborn: A Rare Presentation. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg[Internet]. 2012[cited 14 september 2013]; 64(3): [aprox. 2p.]. Available from: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12070-011-0371-y#page-1
5. Rioboo Crespo MR, Planells del Pozo P, Rioboo García R. Epidemiología de la patología de la mucosa oral más frecuente en niños. Medicina y Patología Oral[Internet]. 2011[citado 14 september 2013]; 10(5): [aprox. 6p.]. Disponible en: http://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=3059193
6. Portelles AM, Torres AT. Quiste dermoide del suelo de la boca. Rev Cubana Estomatol[Internet]. 2010[citado 14 september 2013]; 47(4): [aprox. 3p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0034-75072010000400008&script=sci_arttext
7. Gul A, Gungorduk K, Yildirim G, Gedikbasi A, Ceylan Y. Prenatal diagnosis and management of a ranula. J Obstet Gynaecol[Internet]. 2008 [citado 14 september 2013]; 34(2): [aprox. 3p.]. Disponible en: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1447-0756.2008.00767.x/full
8. Seong-Ha K, Kyung-Hoe H, Chang-Hyeon A, Jin-Woo P, Won-Jin Y. Giant plunging ranula: a case report. Imaging Sci Dent[Internet]. 2013[cited 14 Mar 2013]; 43(1): [aprox. 3p.]. Disponible en: http://synapse.koreamed.org/DOIx.php?id=10.5624/isd.2013.43.1.55
9. Moreira LT, Araujo Júnior E, Marcondes L, Fernandes A, Martins MG. Ránula congénita: diagnóstico ultrassonográfico antenatal. Radiol Bras[Internet]. 2012[citado 29 dic 2014]; 45(5): [aprox. 1p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0100-39842012000500015&lang=pt
10. Samant S, Morton R, Ahmad Z. Surgery for plunging ránula: the lesson not yet learned? Official Journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological[Internet]. 2011[cited 14 September 2013]; 268(10): [aprox. 5p.]. Available from: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00405-011-1509-y/fulltext.html
11. Mihir R, Patel MD, Allison M, Deal MS, William W, Shockley MD. Oral and plunging ranulas: What is the most effective treatment? General Otolaryngology[Internet]. 2009[cited 14 September 2013]; 119(8): [aprox. 8p.]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/enhanced/doi/10.1002/lary.20291/
12. Cabello CJ, García K, Pérez JA. Ránula sublingual: presentación de un paciente. Medicentro[Internet]. 2011[cited 14 September 2013]; 15(3): [aprox. 2p.]. Available rom: http://medicentro.vcl.sld.cu/paginas%20de%20acceso/Sumario/ano%202011/v15n3a11/006ranula97revisado.htm
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


