Autoimmune hemolytic anemia with negative Coombs test
Keywords:
ANEMIA, HEMOLYTIC, AUTOIMMUNE, COOMBS TEST, SEPSISAbstract
Introduction: autoimmune hemolytic anemia is a type of low-grade acquired hemolytic anemia, produced by antibodies against the patient's own erythrocytes leading to their destruction.
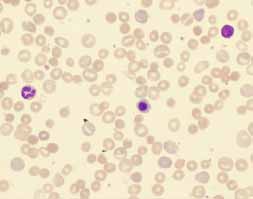
Case report: a 12 year-old female patient arrived in the emergency room for shortness of breath and headache. She noticed colored urine and stools from a week of evolution and 2 days earlier began with severe headache, fever, vomiting, loss of appetite and marked weakness. She was hospitalized due to suspected leptospirosis. Hemoglobin: 50 gl, Hto: 015 L / L. Reticulocyte count: 16x10 -3 / L. Total bilirubin: 63 mmol / L, direct bilirubin: 12 mmol / L, Indirect bilirubin: 51 mmol / L, Coombs direct: negative. Leptospira rapid test: Negative. On the third day: Hemoglobin: 50 gl, Hematocrit: 015 L / l. Erythrocytes: 100 mm / h. Reticulocyte count: 5x10-3. She was transfused, hydrated and underwent antibiotic treatment, employs intacglobin and prednisone. On the seventh day: Coombs direct: IgG positive with activity at 37 ° C. Treatment continued: at day 21 Hemoglobin: 85 g / L, Hematocrit: 0.25 L / L, Reticulocyte count: 200 x 10-3.
Conclusion: sepsis and autoimmune hemolytic anemia was the definitive diagnosis. The caso of this patient constitutes an interesting case to show in the beginning negative test of Coombs that later when imposing the appropriate treatment and diminishing the lysis of erythroid cells, was positive and allowed the diagnosis of certainty which contributed to the good final evolution of the patient.
Downloads
References
1. Jaime Pérez J C, Gómez de León A. Anemia hemolítica autoinmune. In: Pérez J, Almaguer D. Pérez J, Almaguer D Eds. José Carlos Jaime Pérez, and David Gómez Almaguer.eds. Hematología. La sangre y sus enfermedades, 2e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill [Internet] 2014[citado 2016 diciembre 19]. Disponible en: https://hematologiacelular2015.files.wordpress.com/2014/12/hematologia-la-sangre-y-sus-enfermedades.pdf.
2. Céspedes Floirián E, Juy Aguirre E, Valón Rodríguez O, Duverger Domínguez, Rubal Wong A. Anemia hemolítica autoinmune por anticuerpos fríos y drepanocitemia de aparición tardía. MEDISAN [Internet] 2010[citado 2016 dic 19] ; 14 (9):2195. Disponible en: http://bvs.sld.cu/revistas/san/vol_14_9_10/san17910.pdf
3. Alfonso Valdés ME, Bencomo Hernández AB, Hernández Padrón C, Avila Cabrera OM. Síndrome de aglutininas frías y púrpura trombocitopénica autoinmune. Un caso inusual de síndrome de Evans. Revista Cubana de Hematología, Inmunología y Hemoterapia [Internet] 2015[citado 2016 dic 19]; 31(2). Disponible en: http://www.revhematologia.sld.cu/index.php/hih/article/view/302/176.
4. Zeissig Y, Petersen BS, Franke A, Blumberg RS, Zeissig S. Rare phenotypes in the understanding of autoimmunity. Immunology and Cell Biology [Internet] 2016[citado 2016 nov ];94(10):[Aprox.5p.].Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27562064
5. Bencomo Hernández AA, Alfonso Valdés ME, Correa Palmero I, Macías Abraham C, Avila Cabrera OM, Hernández Padrón C. Concentración de autoanticuerpos IgG en hematíes y respuesta al tratamiento en la anemia hemolítica autoinmune. Rev Cubana de Hematología, inmunología y Hemoterapia [Internet] 2013 [citado 2016 dic 19]; 29(2).
Disponible en: http://www.revhematologia.sld.cu/index.php/hih/article/view/42/50
6. Swiecicki PL, Hegerova LT, Gertz M. Cold agglutinin disease. Blood [Internet]; 2013. Disponible en:http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/122/7/1114?sso-checked=true.
7. Bertsias GK, Pamfil C, Antonios Fanouriakis, Boumpas DT. Diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus: has the time come? Nature Reviews Rheumatology [Internet] 2013[citado 2016 dic 19]; 9: 687–694.
Disponible en: http://www.nature.com/nrrheum/journal/v9/n11/full/nrrheum.2013.103.html
8. Alfonso Valdés María Elena, Bencomo Hernández Antonio. Tratamiento de las anemias hemolíticas autoinmunes. Rev Cubana Hematol Inmunol Hemoter [Internet]. 2013 Dic [citado 2017 Jun 16] ; 29( 4 ): 327-339. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-02892013000400003&lng=es.
9. Wright DE, Rosovsky RP, Platt MY. Case 36-2013: A 38-Year-Old Woman with Anemia and Thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. [Internet] 2013[citado 2016 dic 19]; 369 (21):[Aprox.11p].
Disponible en: http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMcpc1215972.
10. Rivero-Jiménez RA. Una mirada al diagnóstico de laboratorio de las enfermedades autoinmunes. Rev Cub Hematol Inmunología y hemoterapia [Internet] 2013 [citado 2016 dic 19]; 29(2). Disponible en: http://www.revhematologia.sld.cu/index.php/hih/article/view/64/45.
11. Henao JA, Valverde K, Ávila ML. Anemia hemolítica como presentación inicial de enfermedad de Wilson: un caso pediátrico. Arch Argent Pediatr [Internet] 2016 [2016 dic 19]; 114(6):e436-e439 / e43. Disponible en: http://www.sap.org.ar/docs/publicaciones/archivosarg/2016/v114n6a27.pdf
12. Brauer DL, Edelman B, Rapoport AP, Hess JR, Akpek G. Plasma exchange and rituximab treatment for lenalidomide-associated cold agglutinin disease. Transfusion. [Internet] 2012 Nov[citado 2016 dic 19];52(11):[Aprox.3p]. Disponible en: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1537-2995.2012.03608.x/abstract
13. Bencomo Hernández AA, Alfonso Valdés M Elena, Ávila Cabrera Onel M, Jaime Fagundo Juan Carlos, Hernández Ramírez Porfirio. Detección y cuantificación de autoanticuerpos en los hematíes de pacientes con anemia hemolítica autoinmune con prueba de Coombs negativa. Rev Cubana Hematol Inmunol Hemoter [Internet] 2005 Dic [citado 2016 dic 19]; 21(3).
Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-02892005000300006&lng=es.
14. Rotenstein L, Nathan A, Ghobrial I, Antin J, and Parnes A. Management of refractory autoimmune hemolytic anemia via allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplantation [Internet] 2016 [citado 2016 dic 19]; 51, [Aprox.2p]. Disponible en: http://www.nature.com/bmt/journal/v51/n11/full/bmt2016152a.html
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


