Clinical diagnosis of acute lymphoid leukemia-T
Keywords:
PRECURSOR CELLS LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA-LYMPHOMA, PEDIATRICS, MEDIASTINUM.Abstract
Introduction: acute lymphoblastic or lymphoblastic leukemia is the most frequent neoplasm in pediatric ages. In childhood, most are B-cells, only 12% to 15% have T-immunophenotype. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia- T is a disease with remarkable clinical and biological heterogeneity that frequently occurs in young adults, usually males, with a high count of white blood cell, mediastinal mass and possible invasion of the central nervous system.
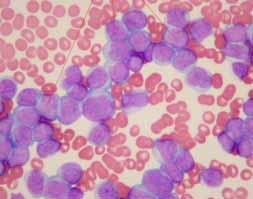
Case Report: a male adolescent with upper right edema, lateral neck region and hemiface of the same side associated with cough, in addition to left peripheral facial paralysis and hepatosplenomegaly. A mediastinal widening with left pleural effusion was evidenced in chest X-ray, the presence of a large tumor mass occupying the anterosuperior and middle part of the mediastinum with left predominance is observed by means of computer axial tomography of the chest. In the clinical laboratory tests, hyper-leukocytosis was observed with 49% of blasts and a marked uric acid as well as LDH increase; the medullogram showed the presence of 90% of lymphoid-like blasts, being confirmed by immunophenotyping approach with the aid of flow cytometry and T-cell lineage.
Conclusions: the nonspecific character of the initial clinical manifestations is highlighted, as indicators of different diagnoses, so it is considered useful and interesting to refer the case to the consideration of other health professionals.
Downloads
References
1. Sima J, Ching-Hon P. Clinical manifestations and treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 6a. ed. Canada: Elsevier S.A; 2013[citado 2017 ene 12]; [Aprox.8p.] Disponible en : http://ascopubs.org/doi/abs/10.1200/jco.1996.14.1.18
2. Raetz E, Lee-Chuen M, O'Brien M, Whitlock J. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. Wintrobe’s Clinical Hematology. (76): 13a. ed New York: Lippincott Williams Wilkins; 2013.
3. Villalba Toquita CP, Martínez Silva PA, Acero H. Caracterización clínico-epidemiológica de los pacientes pediátricos con leucemias agudas en la Clínica Universitaria Colombia. Serie de casos 2011-2014. Pediatr [Internet] 2016 [citado 2017 ene 12];49(1): [Aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0120491216000148.
4. Canadian Cancer Society [Internet] Toronto: Canadian Cancer Statistics; 2014. Disponible en: http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-101/canadian-cancer-statistics-publication/?region=on.
5. Romero Pérez T, Abreu Ruiz G, Luna Morales C, Sierra Pérez D, Gandul Sal L, Planas Labrada R. Programa integral para el control del cáncer en Cuba. Sección independiente de control de cáncer [Internet] Cuba: Editorial Ciencias Médicas; 2012. Disponible en: http://www.paho.org/cub/index.php?option=com_docman&view=download&category_slug=documentacion-tecnica&alias=378-control-del-cancer-en-la-aps-experiencias-cubanas-2009&Itemid=226.
6. Jiménez A, Samudio M, Caniza MA. Factores de riesgo asociados a la sobrevida en niños y adolescentes con leucemia linfoblástica aguda. Pediatr. (Asunción) [Internet] 2016 Abr [citado 2015 ene 20];43(1): [Aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.iics.una.py/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1683-98032016000100003&lng=pt.
7. Vizcaíno M, Lopera JE, Martínez L, De los Reyes I, Linares A. Guía de atención integral para la detección oportuna, diagnóstico, tratamiento y seguimiento de leucemia linfoide aguda en niños, niñas y adolescentes. Rev Colom Cancerol [Internet] 2016 [citado 2015 Ene 20];20 (1): [Aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-revista-colombiana-cancerologia-361-articulo-guia-atencion-integral-deteccion-oportuna-S0123901515000918.
8. Pekarsky Y, Drusco A, Kumchala P, Croce M. The long journey of TCL1 transgenic mice: lessons learned in the last 15 years. Gene Expr [Internet] 2015 [citado 2015 ene 20];16(3): [Aprox. 19 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4963004/
9. Genescà E, Ribera J, Ribera J. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia of T progenitors: from biology to clinics. Med Clín [Internet] 2015; [citado 2015 en 20]; 144(5):[Aprox.5p.] .Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24667111
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


