Socio-demographic and temporal characterization of type-2 diabetes mellitus
Keywords:
Type-2 diabetes mellitus/diagnosis/complications.Abstract
Introduction: type-2 diabetes mellitus constitutes a health problem that affects humankind; therefore research about the topic is necessary considering socio-demographic and temporal aspects.Objetive: to characterize type 2 diabetic people according to socio-demographic variables, years suffering from the disease and the age of onset.
Material and method: a descriptive and cross-sectional, kind of observational study was conducted with the intention of classifying type-2 diabetic people according to socio-demographic variables, years suffering from the disease and age of onset at 119 Doctor's Office, "Hermanos Cruz" University Clinic. The target group included 48 type-2 diabetic people belonging to the health area and the sample was comprised of 45 people. The research was carried out from April 1st, 2009 to April 30, 2010.
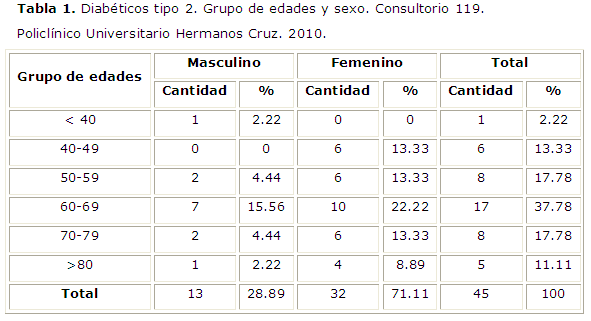
Results: type-2 diabetes mellitus resulted more frequent found in ages from 50 to 79 having a significant prevalence in female sex.
Conclusions: the most important part of the people participating in the study showed less than 10 years of the disease natural history and the onset was frequent in the group of ages from 50-59 and from 40-49.
Downloads
References
1. Rosales González E, Crespo Mojena N, Triana Ponce A, Triana López Y, Palma López M E. Causas de muerte en pacientes diabéticos de Ciudad de La Habana según certificados de defunción. Revista Cubana de Medicina General Integral [Internet]. Enero-Marzo 2008 [citado 2009 Mar 15]; 24 (1). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0864-21252008000100003&script=sci_arttext
2. López I, Mendoza M, Rodríguez C, Álvarez L. Características Clínicas de pacientes con Diabetes Mellitus 2 del Centro de Salud Familiar "Chiguay". Revista Anacem. 2009; 3(1).
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2009. Diabetes care. [Internet] Enero 2009 [citado 2010 Jul 9]; 32(Supl1): [Aprox. 40p.]. Disponible en: http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/32/Supplement_1/S13.full
4. Torres Herrera O. Usted puede. Controlar su diabetes. 1ra ed. La Habana: Editorial Científico Técnica; 2007.
5. Álvarez Sintes R, Hernández Cabrera G, Báster Moro JC, García Núñez RD. Temas de Medicina General Integral. 2da ed. Vol 3. La Habana: ECIMED; 2008.
6. Machado-Alba JE, Moncada-Escobar JC, Gaviria H. Quality and effectiveness of diabetes care for a group of patients in Colombia. Rev Panam Salud Pública. [Internet]. 2009 Diciembre [citado 2010 Jul 10]; 26(6): [Aprox. 6p]. Disponible en: http://www.scielosp.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1020-49892009001200008&lng=en.doi:10.1590/S1020-49892009001200008
7. Del Valle M. Epidemiología de la diabetes. En: XIX Congreso Latinoamericano de Patología Clínica/ML. La Habana: ALAPAC; 2009. p 1-54.
8. Office of Chronic Disease Epidemiology and the South Carolina Diabetes Prevention and Control Program (DPCP) of the Bureau of Community Health and Chronic Disease Prevention and the Diabetes Initiative of South Carolina (DSC). Burden of Diabetes Report 2009. [Internet]. Carolina del Sur: SC DHEC South Carolina Diabetes Prevention and Control Program; 2009 [Citado 2010 Jul 10]. Disponible en: http://www.scdhec.gov/administration/library/CR-009477.pdf
9. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes care. [Internet]. Enero 2010 [citado 2010 Jul 10]; 33(Supl1): [Aprox. 7p.]. Disponible en: http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/Supplement_1 /S62.full
10. Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, et all. Harrison Principios de Medicina Interna. 17ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.; 2009.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


