From cellular therapy to alveolar bone regeneration in post-extraction stage
Keywords:
Stem cells, Regenerative Medicine.Abstract
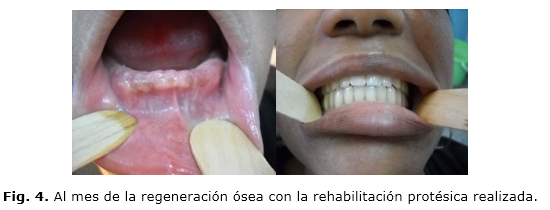
Introduction: post-extraction alveolar resorption is a physiological phenomenon which occurs after teeth extraction. Besides, it reduces the original height and width, in an amount which can vary between different locations and individuals.Case report: patient presenting requiring multiple dental extractions in the mandibular region serving poor oral hygiene, which was found on physical examination, complementary studies were performed. It was decided to place adult stem cells at the level of extraction sockets tooth, prior evaluation and preparation of the patient with the hematology and cross-functional medicine. Surgical medical conduct was described. Graphically it presents the radiological clinical evolution of the patient, immediately, one month and one year later.
Conclusions: issues identified in this study confirm the use of adult stem cells in the regeneration of alveolar bone cavities of the jaws, alveolar process as an effective preservation, as well as opening new perspectives in the treatment of other conditions of the maxillofacial regions anfter fractures, osteoarthritis, injuries and oncological defects, among others; so research projects are to be performed to support the use of cell therapy as warranted.
Downloads
References
1. Raspall G. Patología del esqueleto óseo facial. En: Cirugia maxilo facial. Patología quirúrgica de la cara boca y cuello. Madrid, España: Editorial Panamericana; 2002: 232-36.
2. Villa García LD, Márquez Preciado R. Regeneración dental: el futuro de la odontología. Revista de divulgación de la Universidad Michoacana de san Nicolás de Hidalgo[internet]. 2015[citado mayo 2014]; 75(10). Disponible en: http://www.sabermas.umich.mx/archivo/secciones-anteriores/articulos/75-numero-10/149-regeneracion-dental-el-futuro-de-la-odontologia.html
3. Howard Mora M. Innovaciones en Odontología: la regeneración de los tejidos dentales y el reemplazo biológico de los dientes. Revista científica odontológica[internet]. 2010[citado mayo 2014]; 6(1): Disponible en: http://colegiodentistas.org/revista/index.php/revistaodontologica/article/view/162
4. Santiago Dager E, LaO Salas N, Urgellés Pérez Y, Riesgo Cosme Y, Alí Pérez NA. Ventajas y usos de las células madre en estomatología. MEDISAN[revista en la Internet]. 2014 sep [citado 2015 ene 29]; 18(9): 1282-1292. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1029-30192014000900014&lng=es
5. Betancourt Gamboa K, Barciela Calderón J, Guerra Menéndez J, Cabrera Carballo N. Uso de células madre en el complejo bucofacial. AMC[revista en la Internet]. 2012 oct[citado 2015 ene 29]; 16(5): 651-661. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1025-02552012000500015&lng=es
6. Bansal R, Jain A. Current overview on dental stem cells applications in regenerative dentistry. J Nat Sc Biol Med[serial online]. 2015[cited 2015 Jan 29]; 6: 29-34. Available from: http://www.jnsbm.org/text.asp?2015/6/1/29/149074
7. Munévar Niño JC, Becerra Calixto AP, Bermúdez OC. Aspectos celulares y moleculares de las células madres involucrados en la regeneración de tejidos con aplicaciones en la práctica clínica odontológica. Acta odontol. venez[revista en la Internet]. 2008 dic [citado 2015 ene 29]; 46(3): 361-369. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.ve/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0001-63652008000300023&lng=es
8. Jamal M, Chogle S, Goodi, H, Karam S. Dental Stem Cells and Their Potential Role in Regenerative Medicine. Journal of Medical Sciences[internet]. 2011[cited jan 2014]; 4(2): 53-61. Available from: http://hamdanjournal.org/journal/files/journals/1/issues/14.pdf
9. Rosales Ibáñez R. Ingeniería tisular en Odontología. Revista ADM[internet]. Julio-agosto 2012[citado enero 2014]; LXIX(4): 164-67. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/adm/od-2012/od124d.pdf
10. González Orta LJ. Investigación con células madre de origen dentario. Actualización. Gaceta Dental[internet]. 2011[citado mayo 2014]; 09. Disponible en: http://www.gacetadental.com/2011/09/investigacin-con-clulas-madre-de-origen-dentario-actualizacin-25547/#
11. Valencia R, Espinosa R, Saadia M, Velasco Neri J, Nario H. Panorama actual de las células madre de la pulpa de dientes primarios y permanentes. RODYB[internet]. 2013[citado mayo 2014]; 2(2). Disponible en: http://www.rodyb.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/Celulas-Madre-de-la-Pulpa-de-Dientes-Primarios-y-Permanentes3.pdf
12. Gutiérrez-Ventura F. Células madre en odontología: realidad o ilusión. Rev Estomatol Herediana[internet]. 2014 Abr-jun[citado enero 2015]; 24(2): 61-2. Disponible en: http://www.upch.edu.pe/vrinve/dugic/revistas/index.php/REH/article/view/2125/2115
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


