Reconstruction with fronto-nasal flap in human bite
Keywords:
REHABILITATION, MYOCUTANEOUS FLAP, WOUNDS AND INJURIES, HUMAN BITES.Abstract
Introduction: for many centuries the face has represented the main focus of appearance. The middle facial third, which includes the nose, lower eyelids and the mid-corner area, is the most important area of the face and is therefore extremely vulnerable to posttraumatic facial deformities.
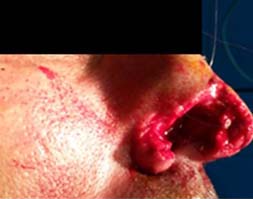
Clinical case: a 44-year-old male patient with no known medical history, consults with the Emergency Department of the Dr. Leon Cuervo Rubio Hospital of Pinar del Río for human bite after aggression, resulting in loss of the right nasal wing, with cartilage involvement and without any treatment. We present clinical aspects related to this case, as well as the type of surgical treatment used for it.
Conclusions: the frontal flap is considered a first-line reconstructive option in the treatment of extensive cutaneous nasal defects. Using tissues with similar characteristics of texture and color allows to offer a wide skin coverage, which makes the fronto-nasal flap especially useful in repairing the nasal wing lost by accident or tumor cause.
Downloads
References
1. R. González-García, L. Navas-Gías, F.J. Rodríguez-Campo, J. Sastre-Pérez. Colgajo frontal. Método sencillo en la reconstrucción de defectos cutáneos nasales extensos Rev Esp Cirug Oral y Maxilofac 2009; 31(1). Barcelona. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1130-05582009000100005
2. Aldana Ubillús C, Cáceres H, García M, García E. Colgajo frontal paramediano en reconstrucción nasal. Rev. Cir. Parag. [Internet]. 2013 [citado 2016 Feb 07]; 37(2): [Aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.iics.una.py/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2307-04202013000200004&lng=es&nrm=iso
3. Arias Soto JC, Abreu Perdomo FA, Ortiz Silveira M, Despaigne Delisle J, Matienzo Vergara SC. Reconstrucción palpebral inferior después de la escisión de tumores malignos. MEDISAN [Internet]. 2013 Jul [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 17(7): [Aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1029-30192013000700016
4. Ebrahimi A, Motamedi MH, Nejadsarvari N, Ebrahimi A, Rasouli HR. Salient Points in Reconstruction of Nasal Skin after Tumor Ablation with Local Flaps. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. [Internet]. 2016 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 9(3): [Aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5064682/
5. Luna SA, Cejudo MP, Mendonça FM, Martínez FMC. O to Z flaps in facial reconstructions. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. [Internet]. 2015 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 90(2): [Aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0365-05962015000200258
6. Agostini T, Perello R, Russo GL, Spinelli G. Through-and-through Nasal Reconstruction with the Bi-Pedicled Forehead Flap. Arch Plast Surg. [Internet]. 2013 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 40(6): [Aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3840183/
7. Ahuja RB, Chatterjee P, Gupta GK, Shrivastava P. Total upper eyelid reconstruction by single staged malar-cheek flap. Indian J Plast Surg. [Internet]. 2014 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 47(1): [Aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4075198/
8. Rossi M, Milia A, Carmisciano M, D’Arpa S, Cordova A, Moschella F. Advancement Perforator Cheek Flap for Aesthetic One-Stage Reconstruction of Postoncological Extended Split-Thickness Defects of the Nasal Sidewall. The Scientific World Journal. [Internet]. 2013 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 2013(2013): [Aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwi1s9KjpLPSAhXmzVQKHTTaAtsQFgggMAE&url=http%3A%2F%2Fdownloads.hindawi.com%2Fjournals%2Ftswj%2F2013%2F169208.pdf&usg=AFQjCNE4TyT4NuThrKH80YhBKRE8EtM3_g
9. ahpeyma A, Khajehahmadi S. Buccinator-based myomucosal flaps in intraoral reconstruction: A review and new classification. National Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery. [Internet]. 2013 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 4(1): [Aprox. 14 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.njms.in/article.asp?issn=0975-5950;year=2013;volume=4;issue=1;spage=25;epage=32;aulast=Rahpeyma
10. Lee JY, Kim JM, Kwon H, Jung SN, Shim HS, Kim SW. Freestyle Local Perforator Flaps for Facial Reconstruction. BioMed Research International. [Internet]. 2015 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; 2015(2015): [Aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2015/707065/
11. Bauer F, Koerdt S, Rommel N, Wolff KD, Kesting MR, Weitz J. Reconstruction of facial defects with local flaps – a training model for medical students? Head & Face Medicine. [Internet]. 2015 [citado 2017 Ene 16]; s/v(s/n): [Aprox. 16 p.]. Disponible en: https://head-face-med.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13005-015-0087-4
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


