Atherogenic markers and metabolic syndrome in the urban population of Pinar del Río
Keywords:
BIOMARKERS, RISK FACTORS, ATHEROSCLEROSIS, METABOLIC SYNDROMEAbstract
Introduction: atherosclerosis, blood vessel disease, is the main cause of cardiovascular disease associated with aging; comprising modifiable risk factors that increase because of this when it exists.
Objective: to evaluate atherogenic markers and metabolic syndrome in older adults, with cardiovascular risk living in urban areas, Pinar del Río province.
Methods: observational, descriptive and cross-sectional study, from the service of Clinical Laboratory at Abel Santamaría Cuadrado Teaching General Hospital Pinar del Río with 60 years old and older patients from the urban areas, during the period 2013 - 2014. The target group included 588 patients. The sample comprised 100 patients who have at least two risk factors previously established for this study.
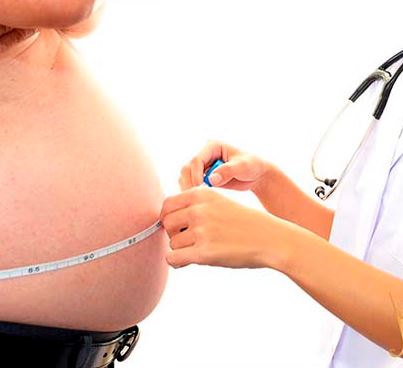
Results: ample predominance of women (61.0 %), the risk factors of higher incidence were hypertension 67 %, and sedentary lifestyle 65 %, followed by obesity 48 %, diabetes mellitus 40 % along with smoking habit 32 %, obese with increased diameters of waist circumference 48 %, and dyslipidemia 49 %, those with high glycemic values in fasting 50 % of the sample. It was considered that 63 % of the patients studied suffer from metabolic syndrome.
Conclusions: a high number of white-skin women, the predominant risk factors were hypertension followed by sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes mellitus and smoking habit. Approximately half of the sample was obese with increased diameters of the waist circumference, a large part suffered from dyslipidemia and half of them showed high fasting blood glucose levels. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was detected.
Downloads
References
1. Goldman L, Schafer AI. Cecil y Goldman Tratado de Medicina Interna. 24a ed. v-1. Barcelona, España: Elsevier España; 2013.
2. Roque C, Nápoles R, Escobar E, Durañones S. Perfil lipídico y factores de riesgo cardiovascular en pacientes geriátricos. Gaceta Medica Espirituana [Internet]. 2012 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 14(2): [aprox. 8p.]. Disponible en: http://bvs.sld.cu/revistas/gme/pub/vol.14.%282%29_15/p15.html.
3. Alonso M, Ferrer M, Carballo R. Factores de riesgo ateroescleróticos en familiares de pacientes diabéticos tipo II. Rev Cubana Inv Bioméd [Internet]. 2014 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 33(4): [aprox. 10p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0864-03002014000400003&script=sci_arttext&tlng=en.
4. Torresani ME, Oliva ML, Rossi ML, Echevarría C, Maffei L. Riesgo cardiovascular según el índice cintura/ talla en mujeres adultas. Actualización en Nutrición [Internet]. 2014 Mar [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 15(1): [aprox. 8p.]. Disponible en: http://www.revistasan.org.ar/pdf_files/trabajos/vol_15/num_1/RSAN_15_1_3.pdf
5. Romero T, Romero CX. Prevención cardiovascular estancada: tendencias alarmantes y barreras socioeconómicas persistentes. Rev Esp Cardiol [Internet]. 2010 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 63(11): [aprox. 9p.]. Disponible en: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0300893210703031?via=sd.
6. Navarrete C, Cartes-Velázquez R, Carrasco C. Dislipidemias en comunidades Peunches de alto Biobo Chileno. Medisan [Internet]. 2013 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 17(1): [aprox. 2p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1029-30192013000100010.
7. Soriguer F, Goday A, Boch Comas A, Bordiu E, Calle A, Carmena R, et al. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in Spain. Diabetologia [Internet]. 2012 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 55(1): [aprox. 6p.]. Disponible en: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00125-011-2336-9#page-1.
8. Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J, IDF Epidemiology Task Force Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome: a new worldwide definition. Lancet [Internet]. 2014 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 366(9491): [aprox. 4p.]. Disponible en: lancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(05)67402-8/abstract.
9. López J, Villar A. Dislipidemias en mayores de 60 años. Rev Cubana Med Gen Integ [Internet]. 2005 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 21(3-4): [aprox. 8p.]. Disponible en: http://www.bvs.sld.cu/revistas/mgi/vol21_3-4_05/mgi043-405.pdf.
10. Farrera/Rozman. Tratado de Medicina Interna. 17a ed. Barcelona, España: Elsevier España; 2012.
11. Bello Rodriguez B, Sánchez Cruz G, Campos Ferreira Pinto A, Báez Pérez EG. Sindrome metaboloico, un problema de salud con múltiples definiciones. Rev Medica Electrón [Internet]. 2012 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 34(2): [aprox. 8p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1684-18242012000200009.
12. Morera Castro YA, González González LM, García Hernández M, Lozada García L. Factores de riesgo ateroescleróticos y comunidad. Rev Cubana Med Integr [Internet]. 2003 Mar-Abr [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 19(2): [aprox. 8p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0864-21252003000200006&script=sci_arttext.
13. de la Fuente Crespo RV, Carballo Martínez RG, Fernández-Britto Rodríguez JE, Guilarte Díaz S, Albert Cabrera MJ. Circunferencia de la cintura con sobrepeso en la HTA en adultos. Revista Habanera de Ciencias Médicas [Internet]. 2012 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 11(5): [aprox. 14p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S1729-519X2012000500011&script=sci_arttext
14. Álvarez Gómez J. El síndrome metabólico y el entrenamiento físico como pilar importante de su tratamiento. Rev Cubana de Cardiol Cir Cardiovasc [Internet]. 2010 [citado 09 Feb 2011]; 16(1): [aprox. 12p.]. Disponible en: http://bvs.sld.cu/revistas/car/vol16_1_10/car07110.htm.
15. Grundy SM. Metabolic syndrome: A multiplex cardiovascular risk factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab [Internet]. 2007 [citado 02 Sept 2015]; 92(2): [aprox. 6p.]. Disponible en: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/92/2/399/2566756
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who have publications with this journal agree to the following terms: Authors will retain their copyrights and grant the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and first publication in this journal are indicated.
Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for distribution of the published version of the work (e.g.: deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a volume). Likewise, and according to the recommendations of the Medical Sciences Editorial (ECIMED), authors must declare in each article their contribution according to the CRediT taxonomy (contributor roles). This taxonomy includes 14 roles, which can be used to represent the tasks typically performed by contributors in scientific academic production. It should be consulted in monograph) whenever initial publication in this journal is indicated. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their web page) before and during the submission process, which may produce interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). https://casrai.org/credit/


